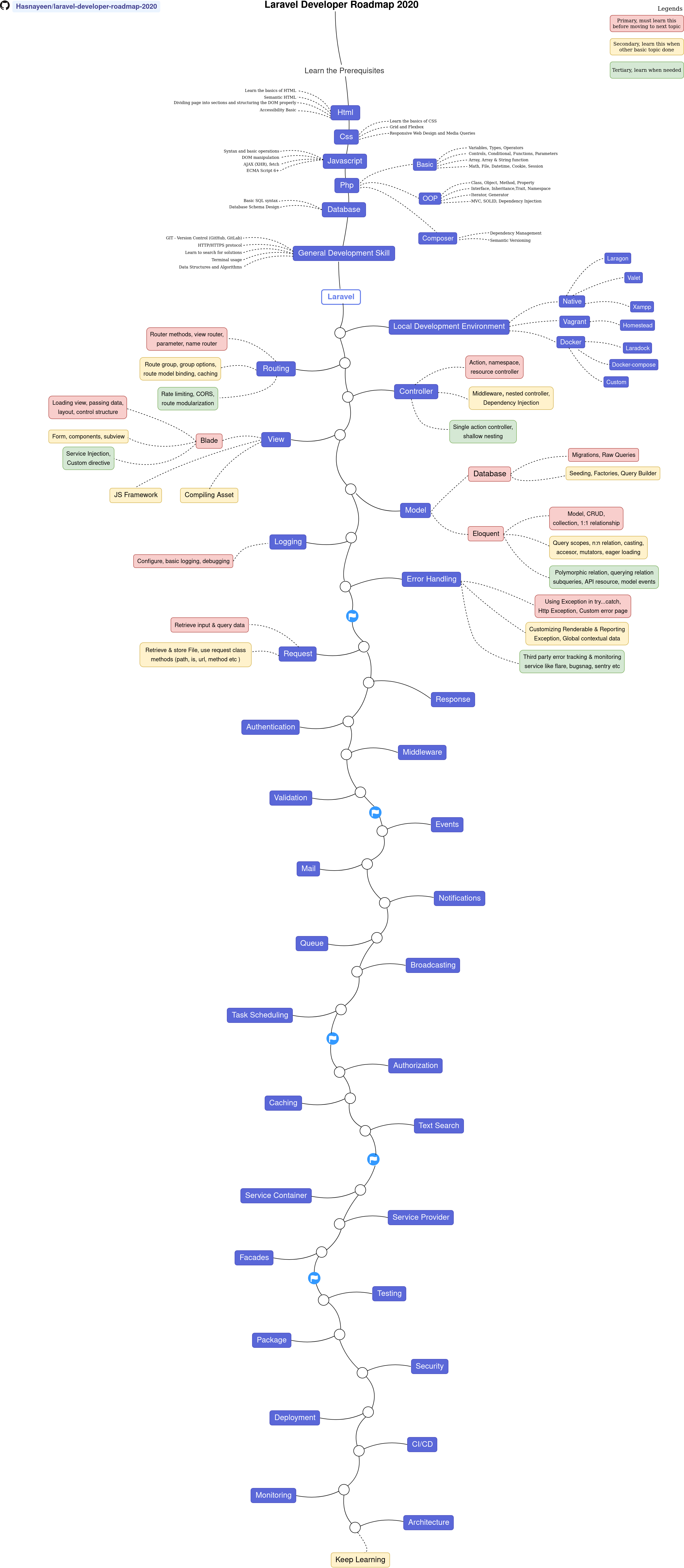
step-by-step flow to start a backend with Laravel
-
Working on a backend team with Laravel can be an exciting and rewarding experience. As a Laravel backend developer, you'll be responsible for building and maintaining the server-side of web applications. Here's a step-by-step guide to getting started and what you can learn on your journey:
Step 1: Getting Started with Laravel
-
Install Prerequisites:
- Make sure you have PHP, Composer, a web server (e.g., Apache or Nginx), and MySQL installed on your development machine.
-
Install Laravel:
- Use Composer to install Laravel by running the following command:
composer global require laravel/installer
- Use Composer to install Laravel by running the following command:
-
Create a New Laravel Project:
- Use the Laravel installer to create a new project:
laravel new <project-name>
- Use the Laravel installer to create a new project:
-
Configure the Environment:
- Set up the database connection in the ".env" file.
- Configure other settings such as app name, timezone, etc.
Step 2: Learn Laravel Basics
-
Routing and Controllers:
- Understand how to define routes in "routes/web.php" and "routes/api.php".
- Create and use controllers to handle requests.
-
Views and Blade Templating:
- Learn about Blade templating engine to create dynamic views.
- Work with layouts, includes, and components.
-
Models and Eloquent ORM:
- Create models to interact with the database using Eloquent ORM.
- Define relationships between models.
-
Database Migrations and Seeders:
- Understand migrations to manage database schema changes.
- Use seeders to populate the database with test data.
-
Middleware:
- Learn how to use middleware to add custom logic to requests and responses.
- Implement authentication and authorization with middleware.
Step 3: Advanced Topics
-
Authentication and Authorization:
- Set up user authentication and learn about Laravel's built-in authentication scaffolding.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC) for user authorization.
-
API Development:
- Build RESTful APIs using Laravel's API resources and request handling.
- Handle validation and error responses.
-
Caching and Performance Optimization:
- Learn about caching to improve application performance.
- Implement caching using Laravel's caching mechanisms.
-
Queues and Jobs:
- Use Laravel's queue system for handling time-consuming tasks.
- Create and dispatch jobs for background processing.
Step 4: Working with a Backend Team
-
Collaborate with Frontend Developers:
- Work closely with frontend developers to define API contracts and data requirements.
- Provide necessary endpoints and data structures for frontend integration.
-
Code Review and Version Control:
- Participate in code reviews to ensure code quality and best practices.
- Use version control (e.g., Git) to collaborate and manage code changes.
-
Unit Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Write unit tests to ensure code correctness and robustness.
- Participate in quality assurance (QA) testing to identify and fix bugs.
-
Documentation:
- Document your code, APIs, and project architecture to facilitate team collaboration and future maintenance.
Remember, learning is an ongoing process. As a Laravel backend developer, you'll continuously encounter new challenges and technologies. Stay curious, keep learning, and be open to exploring new tools and methodologies. Working on a backend team with Laravel can be a fulfilling journey that allows you to create powerful and scalable web applications. Happy coding!
-